In winter seasons there is much need of components like water heaters, gas furnaces and heat pumps. Homeowners who rely on gas furnaces and why they face higher gas bills they thought that it is due to furnace which uses gas. So the truth is that gas and propane only delivers heat modern furnaces also consume electricity for working effectively. That’s why understanding how many watts does a gas furnace use helps you to manage your bills, selecting suitable generators and preparing for power outages.
So in this guide by MileHi HVAC we will explain average wattage and how you can reduce your operating cost by keeping your comfort.
Table of Contents
ToggleAverage watts of a gas furnace
A standard gas furnace normally uses 400 to 1200 watts while running. However many homes have furnaces in the 600 to 800 watt range. But this wattage depends upon different variables like furnace size, efficiency rating and blower motor.
In gas furnaces gas is used as primary source for giving heat and electricity is used for some elements like ignition, airflow and safety concerns. So this system is known as gas furnace wattage which is typical at lower level than electrical heating systems.
Electrical Components and their power use
| Component | wattage | purpose |
| Blower motor | 300–750 watts | Moves warm air |
| Ignition System | 80–120 watts | Lights burners |
| Control Board | 20–50 watts | Manages heating cycle |
| Draft Inducer | 50–100 watts | Vents exhaust |
| Transformer | 10–20 watts | Powers thermostat |
Keep this thing in mind that startup wattage is higher than running wattage. When the furnace starts it draws 1.5 to 2 times than normal operating power. So consider this factor while choosing a backup generator.
At Milehi Hvac, we see many homeowners surprised by their furnace’s electrical needs. Our furnace installation services in Denver include detailed power consumption analysis to help you choose the most efficient system for your home.
Gas Furnace Wattage by Size and BTU Rating

As gas furnace wattage depends upon various factors so gas furnace electricity usage directly depends upon the furnace size. Lager furnaces typically require more powerful blowers which leads to increase in electrical consumption.
BTU and wattage of furnaces
- 40,000-60,000 BTU have wattage of 400-600 watts.
- 60,000-100,000 BTU have wattage of 600-900 watts.
- 100,000-150,000 BTU have wattage of 900-1200 watts.
So high efficiency furnaces which have AFUE ratings above 90% often use variable speed ECM blower motors. These types of motors also reduces electrical demand by 30-50 percent
Average Wattage by Furnace Type
Comparing different heating systems shows why gas furnaces are energy-smart.
| Heating System | Wattage Range | Energy Source |
| Gas Furnace | 400-1,200 watts | Natural gas + electricity |
| Electric Furnace | 10,000-50,000 watts | Electricity only |
| Oil Furnace | 800-1,400 watts | Heating oil + electricity |
| Heat Pump | 3,000-5,000 watts | Electricity only |
| Propane Furnace | 400-1,200 watts | Propane + electricity |
Gas furnaces offer the best balance. They use 400-1,200 watts of electricity while natural gas provides the actual heat. The gas furnace wattage stays relatively low because electricity only powers auxiliary systems.
Electric furnaces are power-hungry. They consume 10,000-50,000 watts because electricity generates all the heat. A typical 15,000-watt electric furnace costs significantly more to operate than a comparable gas unit.
You may read How Long Does A Gas Furnace Last?
Safety and Maintenance | Keep Wattage Low and Equipment Reliable
Maintenance isn’t just about safety; it’s about electrical resistance. When your furnace components are dirty, the mechanical load increases. This directly impacts how many watts a furnace pulls from your panel.
- The Static Pressure Factor: A clogged filter forces the blower motor to work against higher resistance. In our field tests, a furnace with a neglected filter pulled 150 watts more than its rated capacity just to move the same amount of air.
- Capacitor Health: An aging run capacitor can cause a motor to run hot and inefficiently. Replacing a $30 capacitor can prevent a motor from drawing excess amperage and eventually burning out.
- Annual Amperage Checks: During a professional tune-up, a technician should measure the Amp Draw of your blower. If it’s creeping toward the motor’s safety limit, it’s a sign of internal friction or failing bearings.
Factors Increasing Furnace electrical use

Due to the following several factors your furnace will consume more electricity.
Blower Motor
Old motors run on full power with 400 to 800 watts. But modern ECM motors run and use power according to the demand, often using 200 to 600 watts. So this is reducing the gas furnace wattage over time.
Climate and runtime
Electrical consumption also depends upon the time you are using the furnace. Mostly in colder regions, furnaces run all the time almost 8 to 12 hours. So a longer runtime also leads to more usage of electrical power.
Duct Condition and house insulation
Even though the gas is still delivering heat but due to poor insulation and leaky ducts the furnace will run longer cycles compared to normal operating systems. As a result, blower runtime raises gas furnace electrical usage.
Lifespan and maintenance
Regular maintenance matters a lot because with dirty filters and dust buildup electrical usage increases by almost 10-25% so with proper inspection and maintenance the motor will run effectively without any cost.
Why Gas Furnaces Use Far Less Electricity Than Electric Heaters
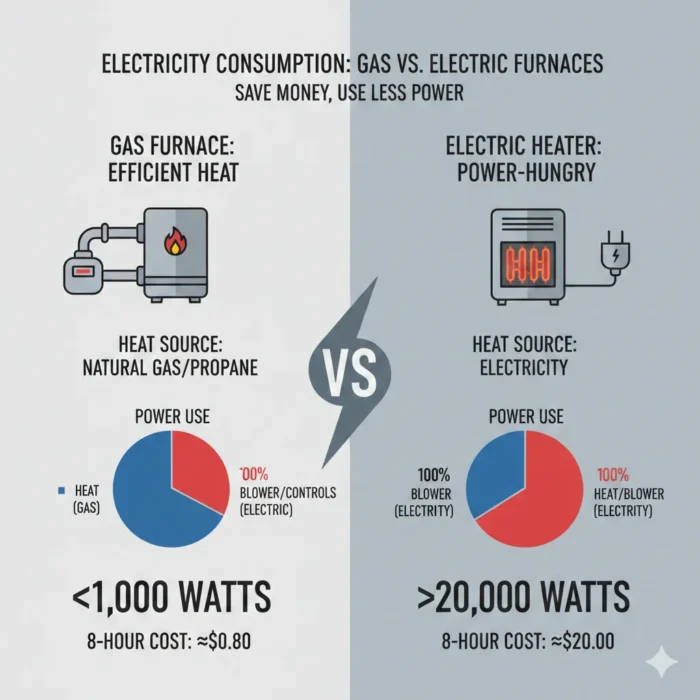
A common misconception is that all furnaces are power hogs. However, when calculating how many watts does a gas furnace use per day, the numbers are surprisingly low compared to electric-only units.
- Heat Source vs. Distribution: In an electric furnace, electricity is the fuel. It uses high-resistance coils (similar to a giant toaster) to create heat. In a gas furnace, natural gas or propane provides the thermal energy.
- The 90/10 Split: For a gas unit, electricity only handles the brains (control board) and the muscles (the blower). This is why a gas furnace typically stays under 1,000 watts, while an electric furnace can easily pull 20,000 watts.
- The Efficiency Gap: If you were to run a gas furnace and an electric furnace for the same 8-hour window, the gas unit would cost you roughly $0.80 in electricity, while the electric unit could cost over $20.00 depending on your local 2026 utility rates.
AFUE vs. SEER and Why Blower Motor Type Matters for Electric Use
While AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) measures how well your furnace converts gas into heat, it doesn’t tell the whole story about your electric bill. To understand the electrical draw, you have to look at the motor technology.
- PSC Motors (Old Tech): These are all or nothing motors. They pull high wattage (approx. 600–800W) regardless of whether your home needs a little heat or a lot.
- ECM Motors (Modern Tech): These Electronically Commutated Motors are the gold standard for 2026. They can ramp down their speed. On a mild day, an ECM motor might only pull 80 watts, significantly lowering the average of how many watts a furnace pulls over a 24-hour period.
- The SEER Connection: If you have a matching AC unit, a high-efficiency furnace blower (ECM) also improves your summer SEER rating by moving air more efficiently across the cooling coils.
Regional Rules, ENERGY STAR, and How Climate Affects Furnace Runtime
Geography is the biggest variable when determining how many watts does a gas furnace use per day.
- The Cold Climate Penalty: In regions like Denver or Minneapolis, a furnace may run for 12–16 hours during a polar vortex. A 600W furnace running for 16 hours consumes 9.6 kWh per day.
- Modern Regulatory Standards: As of 2025, new regional standards heavily favor variable-speed blowers. ENERGY STAR® certified gas furnaces are now required to meet strict Electrical Fan Power (e) ratios, ensuring the blower doesn’t waste electricity while the burners are off.
- Insulation & Cycles: A home with poor envelope insulation causes the furnace to short cycle. Frequent startups are the most expensive part of furnace operation because the startup surge (often 1,500W+) happens more often, spiking your daily consumption.
How Much Does it Cost to Power An Electric Furnace?
In 2026, the average cost to power a standard electric furnace ranges from $350 to $900 per month during the peak winter months. Unlike gas furnaces that use electricity only for auxiliary parts (like the blower), an electric furnace relies entirely on high-wattage heating elements to warm your home. This distinction is the primary reason electric bills skyrocket when the temperature drops.
The Power Breakdown: Kilowatts vs. Watts
While a gas furnace typically stays under 1,000 watts, an electric furnace is a heavy-duty appliance that pulls between 15,000 and 25,000 watts (15–25 kW).
To put this in perspective for a typical 2,000 sq. ft. home:
- Hourly Usage: A 20 kW electric furnace consumes 20 units of electricity (kWh) every hour it runs.
- Daily Cost: In regions like Denver, where electricity rates average $0.15 per kWh, running that furnace for 8 hours a day costs $24.00 per day.
- Monthly Impact: That single appliance can add over $700 to your monthly utility bill—nearly 25 times the electrical cost of a gas-powered unit.
2026 Comparison Table: Operating Costs
| Heating System | Wattage Range | Estimated Daily Cost (8 hrs) | Monthly Budget Impact |
| Electric Furnace | 15,000 – 25,000W | $18.00 – $30.00 | $540 – $900 |
| Gas Furnace (Electricity only) | 400 – 1,200W | $0.48 – $1.44 | $15 – $45 |
| Heat Pump (Average) | 3,000 – 5,000W | $3.60 – $6.00 | $108 – $180 |
Professional Insight: Why Location Matters
In our years of field experience, we’ve found that many homeowners switch to electric heating without realizing that electric furnaces are 100% efficient, yet 300% more expensive to run than gas in cold climates. Because electric units lack the “thermal boost” that gas combustion provides, they must run longer cycles to maintain a consistent temperature in poorly insulated homes.
If you are currently using an electric furnace and notice your costs are higher than the averages above, it is often due to short-cycling. This happens when a thermostat is poorly placed or a filter is clogged, forcing the high-wattage heat strips to click on and off more frequently, which draws a massive “startup surge” of power every time.
You may read How Long Does a Gas Water Heater Last?
Solar Generators for Furnaces
As we move through 2026, solar generators have become a go-to for emergency furnace backup. However, there is a massive difference between supporting a gas furnace and an electric one.
- Gas Furnace (The Easy Match): Since gas provides the heat, you only need to power the blower motor and igniter. A 2,000W to 3,000W solar generator is usually the “sweet spot.” It can handle the initial startup surge (approx. 1,500W–2,000W) and settle into a low running draw of 400W–800W.
- Electric Furnace (The “Power Hog”): Standard solar generators are rarely enough for electric furnaces, which pull 15,000W+. For these, you would need a large-scale, whole-home battery system (like an EcoFlow Delta Pro 3 or a Tesla Powerwall) rather than a portable unit.
- Battery Capacity Matters: Look for a unit with at least 2,000Wh (Watt-hours) of storage. A 2,000Wh battery running a 500W blower motor will last roughly 3–4 hours on a single charge. To survive an overnight Denver blizzard, we recommend adding expandable battery modules.
- Winter Solar Charging: Remember that Colorado winters have fewer “peak sun hours.” To keep your furnace running indefinitely, you’ll need at least 400W–600W of solar panels to recharge the battery as fast as the furnace drains it.
Calculating Your Gas Furnace Electricity Cost

Knowing your actual costs helps with budgeting and generator planning.
Step 1: Find your furnace’s wattage rating on the data plate inside the blower compartment door. Look for voltage and amperage. Multiply these numbers together. A furnace running on 120 volts at 5 amps uses 600 watts.
Step 2: Estimate daily runtime hours. Most furnaces run 6-10 hours per day in winter.
Step 3: Calculate daily kilowatt-hours. Multiply wattage by hours and divide by 1,000. A 700-watt furnace running 8 hours uses 5.6 kWh daily (700W × 8 hours ÷ 1,000).
Step 4: Find your electricity rate on your utility bill. The national average is 17 cents per kWh. Denver residents typically pay 12-14 cents per kWh.
Step 5: Multiply daily kWh by your rate and days per month. That 5.6 kWh furnace costs about 76 cents daily at 13.6 cents per kWh. Over a 30-day month, that’s $22.80 just for the electrical portion.
| Daily Runtime | Monthly kWh (700W furnace) | Monthly Cost (14¢/kWh) |
| 6 hours | 126 kWh | $17.64 |
| 8 hours | 168 kWh | $23.52 |
| 10 hours | 210 kWh | $29.40 |
| 12 hours | 252 kWh | $35.28 |
Picking the Right Generator for Your Furnace
If the electricity fails during winter you won’t want to be left cold. A generator ensures your furnace operates when the power grid is, off.
What Size Is Necessary? Calculate your furnace’s wattage during operation. Then increase that by 25%. This additional margin accounts, for the power spike when the motor starts. For example with a 700-watt furnace your generator should supply least 875 watts.
What Individuals Truly Purchase:
- For furnaces using 400-600 watts opt for a generator rated, between 1,500 and 2,000 watts.
- Sized models that consume 600-900 watts—opt for 2,000 to 2,500 watts instead
- Larger furnaces, with 900-1,200 watts—ideally you need 3,000 to 3,500 watts
The majority of households manage well with a 2,000-watt generator. It can operate your furnace. Still provide sufficient power for a few lights and your refrigerator when the rest of the power is out.
If you want the whole house covered, standby generators start around 7,500 watts. These things kick on automatically when the power drops and can handle your entire electrical panel without you lifting a finger.
How to Reduce Furnace Energy Consumption
- Use a variable speed ECM motor
- Replace air filters every month
- Seal the duct leaks
- Install a small thermostat
- Schedule annual maintenance with professionals
When replacement time comes, Milehi Hvac offers furnace installation services in Denver with detailed energy savings analysis.
Conclusion
A typical gas furnace uses 400–1,200 watts of electricity with most homes averaging 600–800 watts during operation. This adds roughly $20–40 per month to winter electricity bills.
Knowing how many watts does a gas furnace use allows homeowners to budget accurately, select proper backup power and make informed efficiency upgrades. With proper maintenance and modern equipment, gas furnaces remain one of the most cost-effective heating solutions available.
Need expert help choosing an energy-efficient furnace? Contact Milehi Hvac for professional furnace installation services in Denver. We’ll help you find the perfect system to reduce costs and keep your home warm all winter.
FAQs
Will a 2000-watt generator run a gas furnace?
Yes, a 2000-watt generator handles most residential gas furnaces comfortably. Standard furnaces use 600-800 running watts with starting surges around 900-1,200 watts. This leaves enough capacity for a few lights and small appliances.
How many amps does a gas furnace use?
Gas furnaces typically draw 5-15 amps at 120 volts. Smaller units use 5-8 amps while larger systems with powerful blowers draw 10-15 amps. High-efficiency models with ECM motors often use fewer amps.
Can a gas furnace run without electricity?
No, modern gas furnaces cannot operate without electricity. They need power for the ignition system, blower motor, and safety controls. Even though natural gas provides the heat, electrical components are essential for safe operation.
Can a 3500 watt generator run a gas furnace?
Yes, a 3500-watt generator can run most gas furnaces since they mainly power the blower and controls. Make sure it can handle the furnace’s startup (surge) wattage.
Can I plug my gas furnace into a generator?
Yes, but only through a proper transfer switch or interlock for safety. Never plug directly into an outlet without approved electrical protection.
Will a 5000 watt generator run a gas furnace?
Yes, a 5000-watt generator can easily run a gas furnace and other essentials. It provides enough capacity for startup surges and additional appliances.



